What is NAFLD? (and 5 ways to support metabolic health)
WHAT IS NAFLD?
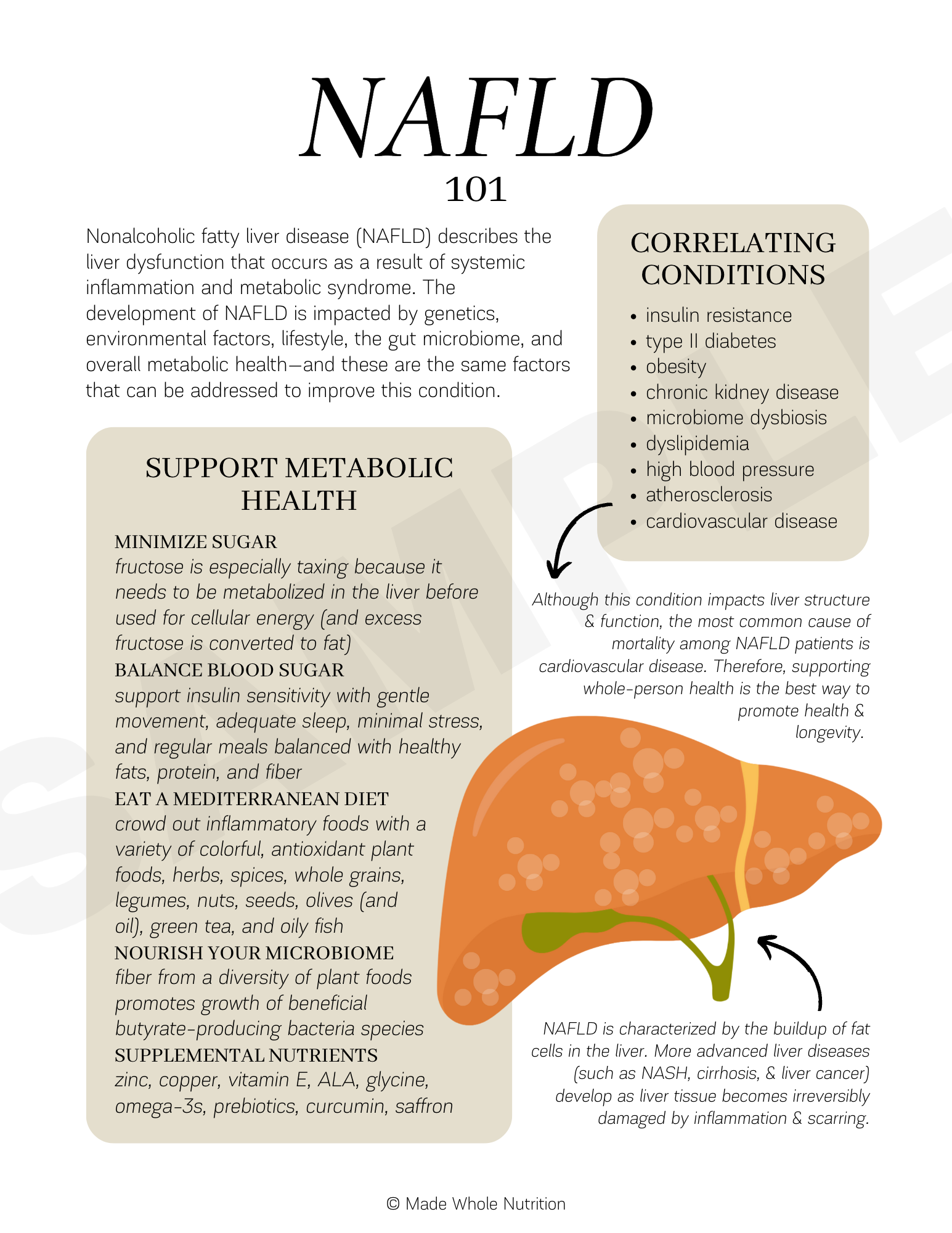
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) describes the liver dysfunction that occurs as a result of systemic inflammation and metabolic syndrome.
The development of NAFLD is impacted by genetics, environmental factors, lifestyle, the gut microbiome, and overall metabolic health—and these are the same factors that can be addressed to improve this condition.
NAFLD is characterized by the buildup of fat cells in the liver. More advanced liver diseases (such as NASH, cirrhosis, & liver cancer) develop as liver tissue becomes irreversibly damaged by inflammation & scarring.
CONDITIONS CORRELATING WITH NAFLD
obesity
chronic kidney disease
cardiovascular disease
Although this condition impacts liver structure & function, the most common cause of mortality among NAFLD patients is cardiovascular disease. Therefore, supporting whole-person health is the best way to promote health & longevity.
WAYS TO SUPPORT METABOLIC HEALTH
EAT A MEDITERRANEAN DIET
crowd out inflammatory foods with a variety of colorful, antioxidant plant foods, herbs, spices, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olives (and oil), green tea, and oily fish
NOURISH YOUR MICROBIOME
fiber from a diversity of plant foods promotes growth of beneficial butyrate-producing bacteria species
SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRIENTS
zinc, copper, vitamin E, ALA, glycine, omega-3s, prebiotics, curcumin, saffron
MINIMIZE SUGAR
fructose is especially taxing because it needs to be metabolized in the liver before used for cellular energy (and excess fructose is converted to fat)
BALANCE BLOOD SUGAR
support insulin sensitivity with gentle movement, adequate sleep, minimal stress, and regular meals balanced with healthy fats, protein, and fiber
Are you a health educator that wants to use this content with your clients? Customize the handout template in less time than it would take to even think about hiring a graphic designer.
References
Berná, G., & Romero-Gomez, M. (2020). The role of nutrition in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiology and management. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver, 40 Suppl 1, 102–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14360
Byrne, C. D., & Targher, G. (2015). NAFLD: a multisystem disease. Journal of hepatology, 62(1 Suppl), S47–S64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.012
Chakravarthy, M. V., Waddell, T., Banerjee, R., & Guess, N. (2020). Nutrition and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Perspectives. Gastroenterology clinics of North America, 49(1), 63–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2019.09.003
Chashmniam, S., Mirhafez, S. R., Dehabeh, M., Hariri, M., Azimi Nezhad, M., & Nobakht M. Gh, B. F. (2019). A pilot study of the effect of phospholipid curcumin on serum metabolomic profile in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 73(9), 1224–1235. https://doi-org.uws.idm.oclc.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0386-5
Chen, J., & Vitetta, L. (2020). Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(15), 5214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155214
Friedman, S. L., Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A., Rinella, M., & Sanyal, A. J. (2018). Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nature medicine, 24(7), 908–922. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
Haigh, L., Kirk, C., El Gendy, K., Gallacher, J., Errington, L., Mathers, J. C., & Anstee, Q. M. (2022). The effectiveness and acceptability of Mediterranean diet and calorie restriction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland), 41(9), 1913–1931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2022.06.037
Meroni, M., Longo, M., Rustichelli, A., & Dongiovanni, P. (2020). Nutrition and Genetics in NAFLD: The Perfect Binomium. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(8), 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082986
Pour, F. K., Aryaeian, N., Mokhtare, M., Mirnasrollahi Parsa, R. S., Jannani, L., Agah, S., Fallah, S., & Moradi, N. (2020). The effect of saffron supplementation on some inflammatory and oxidative markers, leptin, adiponectin, and body composition in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. Phytotherapy Research : PTR, 34(12), 3367–3378. https://doi-org.uws.idm.oclc.org/10.1002/ptr.6791
Tanase, D. M., Gosav, E. M., Costea, C. F., Ciocoiu, M., Lacatusu, C. M., Maranduca, M. A., Ouatu, A., & Floria, M. (2020). The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Journal of diabetes research, 2020, 3920196. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3920196
Tilg, H., Adolph, T. E., Dudek, M., & Knolle, P. (2021). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the interplay between metabolism, microbes and immunity. Nature metabolism, 3(12), 1596–1607. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00501-9
Vancells Lujan, P., Viñas Esmel, E., & Sacanella Meseguer, E. (2021). Overview of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and the Role of Sugary Food Consumption and Other Dietary Components in Its Development. Nutrients, 13(5), 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051442