Functional Nutrition for Mitochondrial Health
POWERHOUSES OF THE CELL
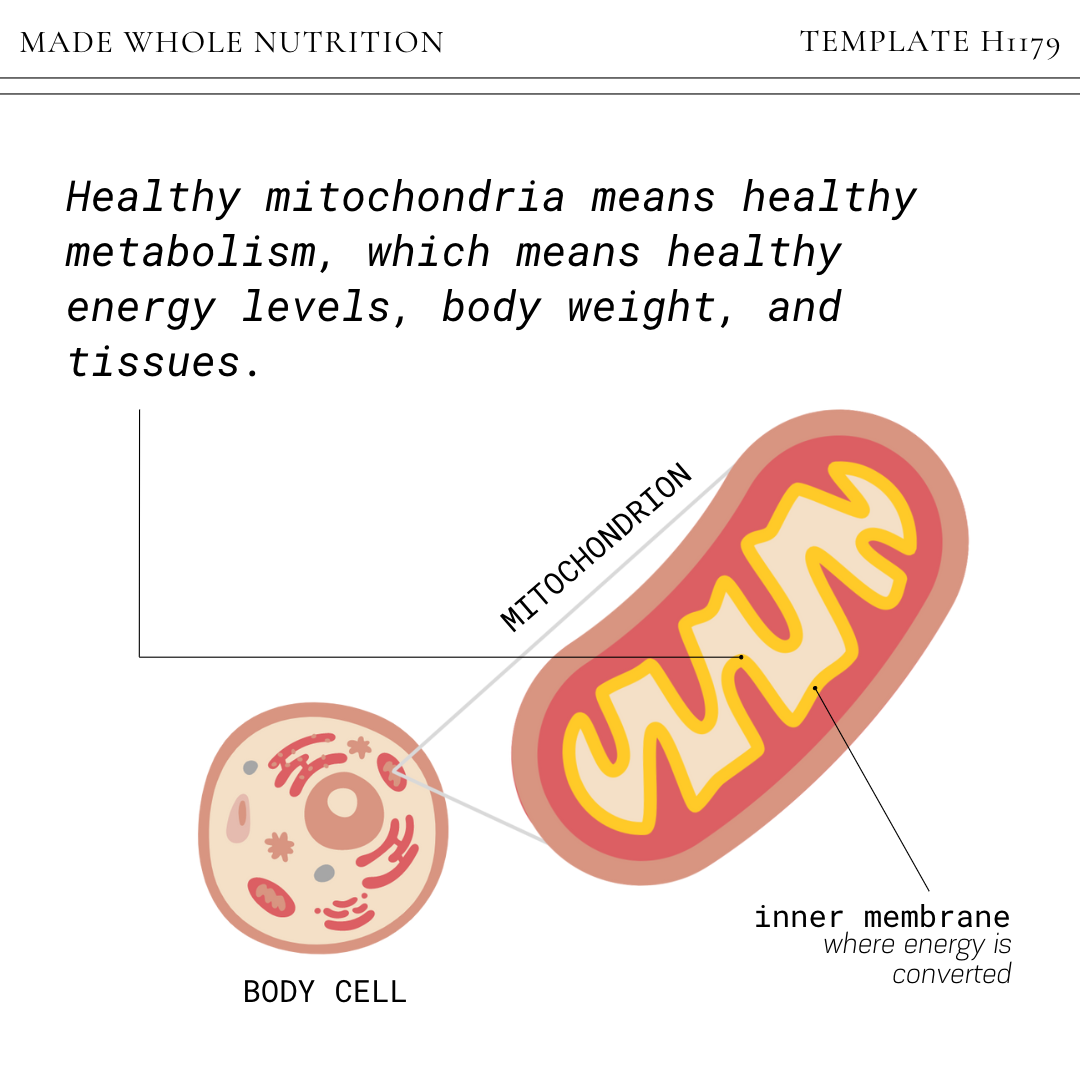
Mitochondria are the parts of your cells that convert caloric energy from food into ATP energy, the form that your body can use.
Because your body cannot store this ATP form of energy, your mitochondria work around the clock to keep your body running (and produce your body weight in ATP every day)!
Healthy mitochondria means healthy metabolism, which means healthy energy levels, body weight, and tissues.
NUTRITIONAL WEALTH
If calories are like "fuel" for your cellular engines, certain vitamins & minerals are like the spark plugs, oil, fuel line, exhaust valve...everything needed to burn that fuel.
This is why eating a poor diet leads to weight gain & lethargy, despite having plenty of caloric energy.
You can promote healthy metabolism by eating a diet full of colorful, nutrient-dense, whole foods.
FRAGILE STRUCTURES
Many diseases & signs of aging (from gray hair to cancer) have been connected to impaired mitochondria.
Limiting exposure to things that cause mitochondria and DNA damage is important for protecting these fragile structures.
DIET & MITOCHONDRIAL HEALTH
Processed sugar & oils, chemicals, alcohol, smoking, air pollution, medications, pesticides, and sunburn are all destructive to your mitochondria.
Antioxidants from fruits & vegetables can help protect against this inflammatory damage, hence their “anti-aging" effects.
SUPPORT HEALTHY MITOCHONDRIA
EAT WHOLE FOODS
mitochondrial health is dependent on healthy levels of minerals, B vitamins, and antioxidants from food
MOVE + SLEEP
just like building muscle, regular movement (esp weight training) and adequate sleep build healthy mitochondria
TRY INTERMITTENT FASTING
intermittent fasting gives the body time to recycle old and build new mitochondria (not recommended for menstruating women)
SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRIENTS
CoQ10, L-carnitine, alpha-lipoic acid
Are you a health educator that wants to use this content with your clients? Customize the handout template in less time than it would take to even think about hiring a graphic designer.
References
Pizzorno J. (2014). Mitochondria-Fundamental to Life and Health. Integrative medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), 13(2), 8–15.
Jones, D. S., Bland, J. S., & Quinn, S. (2010). Textbook of Functional Medicine. Institute for Functional Medicine.Gaby, A. R. (2017). Nutritional Medicine (2nd ed.). Fritz Perlberg Publishing.
Herst, P. M., Rowe, M. R., Carson, G. M., & Berridge, M. V. (2017). Functional Mitochondria in Health and Disease. Frontiers in endocrinology, 8, 296. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00296 Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5675848/