COMMON FOOD ADDITIVE GUIDE - "yay" or "nay" according to a functional nutritionist
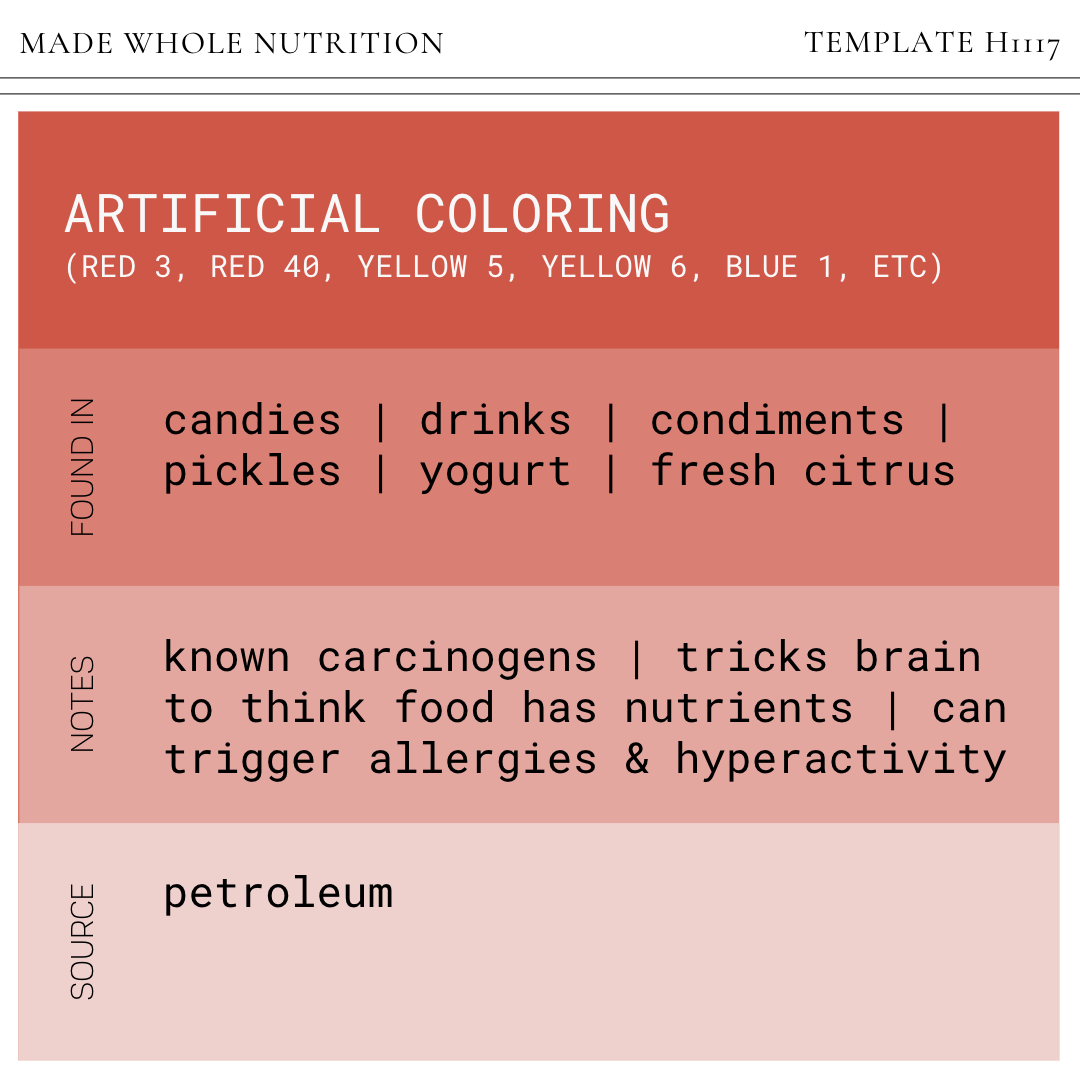
ARTIFICIAL COLORING
(Red 3, Red 40, Yellow 5, Yellow 6, Blue 1, etc)
FOUND IN: candies, drinks, condiments, pickles, yogurt, fresh citrus
SOURCE: petroleum
NOTES: tricks brain to think food has nutrients; known carcinogens; can trigger allergies & hyperactivity
RATING: significant concern, reduce at all cost
ARTIFICIAL SWEETENERS
(sucralose, aspertame, saccharin, acesulfame)
FOUND IN: "sugar-free" products, gum, drinks
SOURCE: chemically produced
NOTES: most reported negative side-effects of all food additives; promote weight gain & blood sugar issues
RATING: significant concern, reduce at all cost
HIGH FRUCTOSE CORN SYRUP
FOUND IN: baked goods, bread, drinks, candies, ice cream, syrup
SOURCE: corn
NOTES: a cheap/ideal form of sugar for food production; promotes weight gain, blood sugar issues, & inflammation
RATING: significant concern, reduce at all cost
HYDROGENATED OILS
(aka trans fat)
FOUND IN: baked goods, crackers, chips, margarine
SOURCE: chemically produced
NOTES: promote inflammation, cardiovascular issues, weight gain, & blood sugar issues
RATING: significant concern, reduce at all cost
MSG
(monosodium glutamate)
FOUND IN: processed & restaurant food, canned soup, Asian food
SOURCE: fermented sugar
NOTES: enhances umami flavor; can trigger nervous system symptoms (migraines, numbness)
RATING: significant concern, reduce at all cost
CARRAGEENAN
FOUND IN: dairy & gluten free products, nut milks
SOURCE: red seaweed
NOTES: thicken & blend food products; appears to promote inflammation, gut issues, & glucose intolerance
RATING: moderate concern, reduce when possible
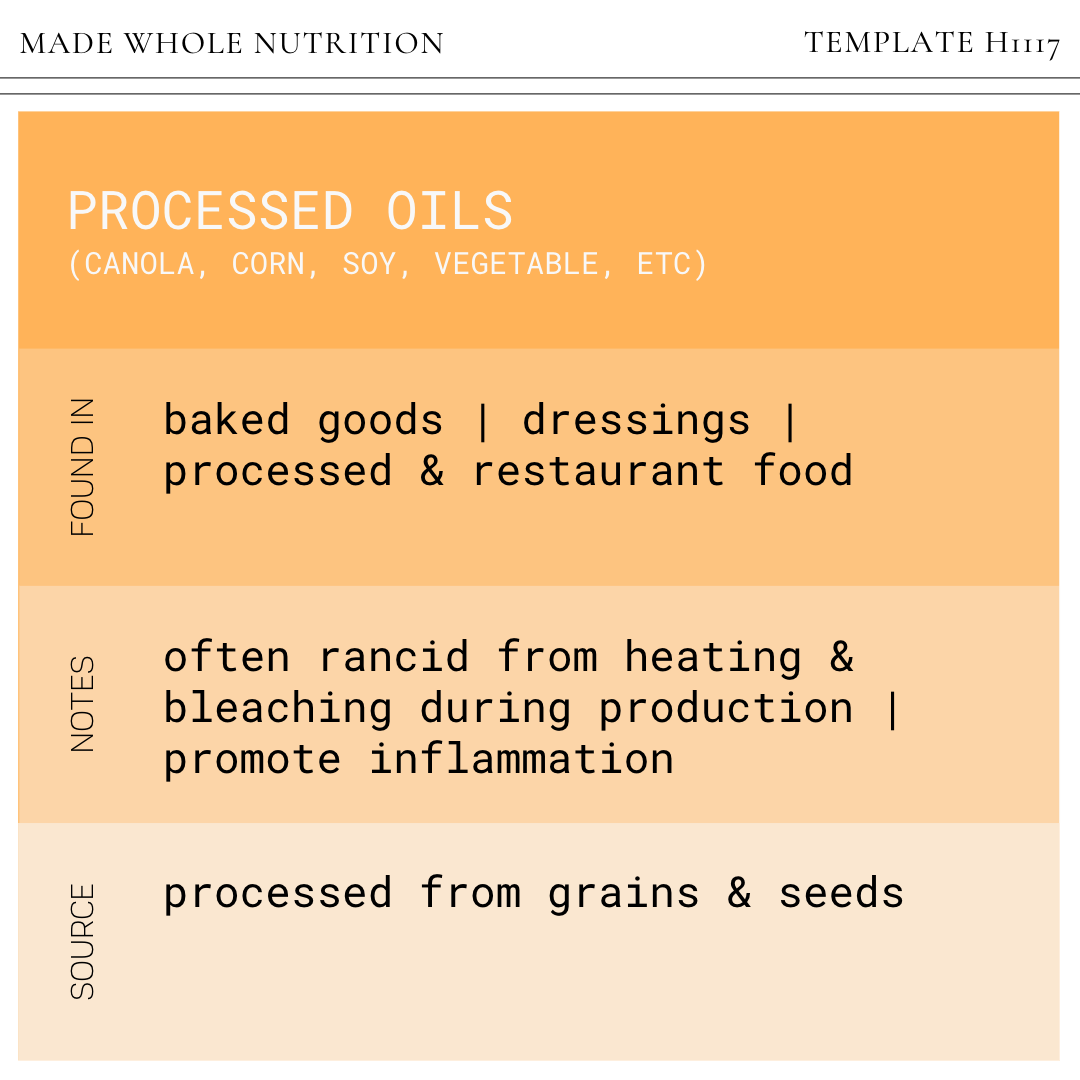
PROCESSED OILS
(canola, corn, soy, vegetable, etc)
FOUND IN: baked goods, dressings, processed & restaurant food
SOURCE: processed from grains & seeds
NOTES: often rancid from heating & bleaching during production; promote inflammation & cardiovascular issues
RATING: moderate concern, reduce when possible
SODIUM BENZOATE
FOUND IN: carbonated drinks, juices, condiments, dressings
SOURCE: chemically produced
NOTES: can trigger hyperactivity; with citric/ascorbic acid it converts to carcinogenic benzene
RATING: moderate concern, reduce when possible
SODIUM NITRITE
FOUND IN: processed meat
SOURCE: chemically produced
NOTES: antioxidant to prevent bacterial growth & retain pink color in meat; converts to carcinogenic nitrosamine
RATING: moderate concern, reduce when possible
SUGAR ALCOHOLS
(xylitol, erythritol, sorbitol, anything that ends in -itol)
FOUND IN: "sugar-free" products, gum, drinks
SOURCE: processed plant sugars
NOTES: promote cravings & blood sugar issues; can cause digestive issues in large amounts
RATING: moderate concern, reduce when possible
CITRIC ACID
FOUND IN: sweetened drinks, candy, jelly, ice cream, canned fruit
SOURCE: Aspergillus niger (black mold)
NOTES: flavor & preserve food products; can be inflammatory for some people sensitive to mold
RATING: minimal concern, some people may need to reduce
FOOD STARCH
(cornstarch, maltodextrin, corn syrup solids, etc)
FOUND IN: baked goods, processed food, dairy & gluten free products
SOURCE: corn, potato, tapioca, wheat
NOTES: blend & thicken food products; GF unless indicated as wheat starch; can be allergenic for some people
RATING: minimal concern, some people may need to reduce
GUMS
(guar, xanthan, gellan, tara, carob, etc)
FOUND IN: dairy & gluten free products, nut milks
SOURCE: soy, corn, wheat; legumes
NOTES: thicken, blend, & bind food products; feed gut microbes (for better or worse, depending on person)
RATING: minimal concern, some people may need to reduce
LECITHIN
FOUND IN: chocolate, ice cream, baked goods, supplements
SOURCE: soy, sunflower, canola, egg
NOTES: blends food products; aka as phosphatidylcholine supplement; minimally allergenic if from soy
RATING: minimal concern, some people may need to reduce
YEAST EXTRACT
FOUND IN: cheese products, salty foods, canned soup
SOURCE: yeast
NOTES: enhances umami flavor; often used in place of MSG; often found in small amounts
RATING: minimal concern, some people may need to reduce
Are you a health educator that wants to use this content with your clients? Customize the handout template in less time than it would take to even think about hiring a graphic designer.
References
Kobylewski, S., & Jacobson, M. F. (2012). Toxicology of food dyes. International journal of occupational and environmental health, 18(3), 220–246. https://doi.org/10.1179/1077352512Z.00000000034
Lindseth, G. N., Coolahan, S. E., Petros, T. V., & Lindseth, P. D. (2014). Neurobehavioral effects of aspartame consumption. Research in nursing & health, 37(3), 185–193. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.21595
Walton, R. G., Hudak, R., & Green-Waite, R. J. (1993). Adverse reactions to aspartame: double-blind challenge in patients from a vulnerable population. Biological psychiatry, 34(1-2), 13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(93)90251-8
12 Common Food Additives. (2018). Healthline. Retreived from: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/common-food-additives
Bhattacharyya, S., Feferman, L., & Tobacman, J. K. (2015). Carrageenan Inhibits Insulin Signaling through GRB10-mediated Decrease in Tyr(P)-IRS1 and through Inflammation-induced Increase in Ser(P)307-IRS1. The Journal of biological chemistry, 290(17), 10764–10774. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.630053
Sweis, I. E., & Cressey, B. C. (2018). Potential role of the common food additive manufactured citric acid in eliciting significant inflammatory reactions contributing to serious disease states: A series of four case reports. Toxicology reports, 5, 808–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.08.002